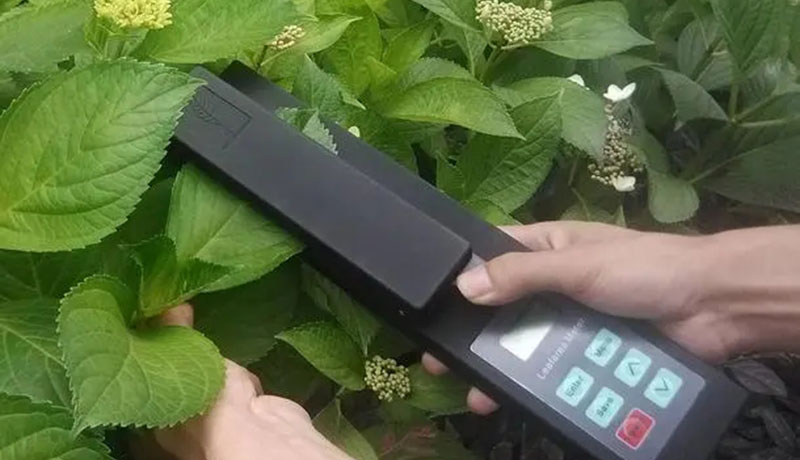
How to Measure Crop Leaf Area, Leaf Area Index, Leaf Thickness And Leaf Angle
Determination of crop leaf area, leaf area index, leaf thickness and leaf angle
Step#1:
Leaves are the primary place for producing organic matter. The level of crop yield is positively correlated with the size of leaf area within a certain range. Usually, the size of leaf area of a crop group is measured by the leaf area index, that is, a certain land area. The total area of crop leaves is equivalent to a multiple of the ground on the ground.
Leaf area index= Leaf area/ land area
The larger the leaf area index, the larger the leaf area per unit land area. However, the larger the leaf area index is, the better. Each crop will have a suitable leaf area index at different growth periods, and its suitable range is closely related to the variety, climate and other conditions.
There are many methods for measuring leaf area, and their accuracy differs. Therefore, specific analysis and necessary explanations should be made in applying this information and specific measurements.
Step#2:Materials and Utensils
Feed ruler, leaf area meter, planimeter, record form, blast drying oven, torsion balance (1% g), dryer, screw micrometer and fabric thickness gauge.
Step#3:Determination method
Methods for measuring leaf area:
The methods for measuring leaf area of crops vary from crop to crop, and the following are commonly used.
Paper sample weighing method:
The sampled leaves at each point (except the undeveloped and orange leaves) are laid on a sheet of paper with uniform thickness (the uniformity of the paper can be measured by cutting paper pieces of the same size in advance and weighed),
Use trace the pencil along the edge of the leaf, and then use scissors to cut out the leaf shape drawn by the pencil, or use engineering printing drawings to make the leaf shape and cut it out. All are weighed to obtain W1, and another paper with a known area of
A1 is taken and weighed to obtain W2 then the leaf area A2 is:
A2=(A1*W1)/W2
Heavier than leaf method:
Fresh weight method: Weigh all the fresh leaves sampled, select 10 large and small leaves each, stack them up, and use two types of cardboard (or wood, glass) of known area respectively , pressed on the folded blade, carefully cut along the edge of the cardboard with a blade, and weighed the sample in a certain area on a torsion balance.
Or after punching with a hole punch of known area, weigh the punched circle. After calculation, the specific leaf weight value (g/cm2) was obtained, and the average specific leaf weight (g/cm2) was obtained after the average of the two values.
Sample leaf area(m2)=Sample leaf weight/average specific leaf weight (g/cm2)
In the formula, 0.0001 is the conversion factor for converting square centimeters into square meters.
Dry weight method:
According to the above method, measure the dry weight of the leaves with known area and the remaining leaves after cutting, obtain the average specific leaf weight (g/cm2), and then obtain the leaf area of the sampling point.
Determination method of leaf area meter:
There are currently various models of leaf area, including a desktop leaf area meter and a portable leaf area meter.
The domestic GCY-200 photoelectric area measuring instrument is introduced here. The principle is: that when the uniform light source illuminates the frosted glass of the leaf area meter, it becomes a uniform diffuse bright surface due to diffuse reflection.
As indicated by the microammeter, if the measured blade is placed on a uniform bright surface, the area of the bright surface will decrease accordingly, and the current generated on the photovoltaic cell will also decrease accordingly. The measurement relationship is as follows:
M/A=cm2/μA
In the formula:
M (cm2) – bright surface area
A (μA)——When the blade is not placed, the photocurrent reading (μA) generated by the bright surface M imaged on the photocell
Y——The current reading when the blade is placed under the bright surface (μA)
X=M-M/A*Y
X – leaf area,
Using the leaf area meter, after the North Korean instrument is adjusted, clamp the tested leaf into the plexiglass clip and insert it under the frosted glass bright panel, and the leaf area value can be directly read from the micro ammeter.
The leaf area measured by the GCY-200 leaf area meter is small, and the large leaves need to be cut into pieces, which is slower in actual work.
The L1-3000 leaf area meter can automatically display numbers and has a high working order, but the price is higher.
Calculator method
- After tracing the leaf shape of the leaf sample on the paper:
- Use the plotter to measure the area one by one.
- Start from a certain point marked with the tip of the instrument.
- Describe a circle clockwise along the leaf edge.
- Return to the original starting point.
- Record the reading, each leaf is measured twice.
The average of the two readings within the allowable error range is the leaf area value of the leaf. Register on the record leaf by leaf.
This method is more accurate and time-consuming. It is often used as a standard method to test the degree of deviation of other methods. It can also be combined with the dry weight method to reduce the workload.
Length×width product coefficient method:
The product of length × width is often larger than the actual leaf area, so there must be a positive coefficient.
For the correction coefficient calculation, the actual area of a large number of leaves is generally measured by a standard method (plotter or area meter) and then removed by the corresponding length × width product. The K value is obtained leaf by leaf, and the average value of K is obtained.
K= Actual leaf area/(length*width)
Leaves of different crops or leaves of different parts of the same crop at different times. The correction coefficients may be different for different periods. Before applying this method, it is necessary to obtain the K value of the leaf area of the tested crop varieties.
Linear regression method: This method is suitable for in vivo measurement with relatively regular leaf shape and good leaf symmetry. Each leaf only needs to measure one data to return to the room for calculation.
The method is to measure the length between certain points, such as the length or leaf width, etc., of the leaves of a certain shape, square the value of the period length, and now calculate according to the regression equation.
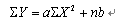
Where: a is the regression coefficient.

